Answer
![\begin{gathered} \sec \theta=\frac{\sqrt[]{53}}{7} \\ \csc \theta=\frac{\sqrt[]{53}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wd33fdajba1vlmk6pbwugx2nvi4hdvgtn8.png)
Step-by-step explanation
The trigonometric function tangent is defined as follows:
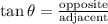
Where
"opposite" refers to the side across the angle θ in the right triangle
"adjacent" refers to the side next to the angle θ in the right triangle
The secant is the reciprocal function of the cosine:
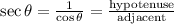
The cosecant is the reciprocal function of the sine:
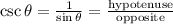
To calculate the cosecant and secant, the first step is to determine the length of the hypothenuse of the triangle.
Considering the given tangent:
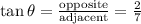
We know that the legs of the triangle have a measure 2units and 7units, using the Pythagorean theorem, we can calculate the length of the hypothenuse:
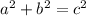
![\begin{gathered} 2^2+7^2=c^2 \\ 4+49=c^2 \\ 53=c^2 \\ \sqrt[]{53}=\sqrt[]{c^2} \\ \sqrt[]{53}=c \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8abdj6rremu728v40lfwx8sxgh6fobdpwc.png)
So,
Opposite=2
Adjacent=7
Hypotenuse =√53
Secant:
![\begin{gathered} \text{sec}\theta=(hypotenuse)/(adjacent) \\ \sec \theta=\frac{\sqrt[]{53}}{7} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8k91zp1cwyeg62fm6lnm7sk4ubg9xr03jy.png)
Cosecant:
![\begin{gathered} \csc \theta=\frac{\text{hypotenuse}}{\text{opposite}} \\ \csc \theta=\frac{\sqrt[]{53}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/bhibjpnk8l9id6l4ncdqklw8f2agp9gmpo.png)