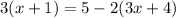
To solve the given equation:
1. Remove parenthesis:
Use distributive property:
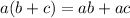
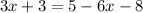
2. Combine like terms:
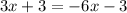
3. Substract 3 in both sides of the equation:
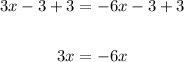
4. Add 6x in both sides of the equation:
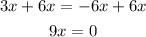
5. Divide into 9 both sides of the equation: (0 divided into any number is equal to 0)
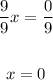
6. Prove the x=0 in the original equation:
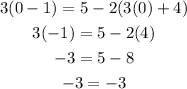
As x=0 make a true the equation (-3 is equal to -3). The solution is correct
The solution for the equation is x=0