Given the function:
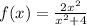
when x=-2, f(x) = ?
Substitute the value of -2 for x in the f(x) function.
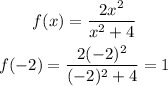
when x = -1, f(x) =?
Substitute the value of -1 for x in the f(x) function.
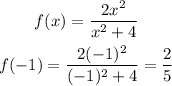
when x = 5, f(x) =?
Substitute the value of 5 for x in the f(x) function.
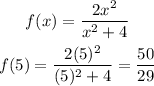
when x = 6, f(x) =?
Substitute the value of 6 for x in the f(x) function.
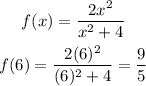
Thus, we have
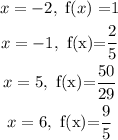
The graph of the f(x) function is as shown below: