Answer:
0.281 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
Volume (V) = 2.50 L.
Temperature (T) = 325.0 K.
Pressure (P) = 3.00 atm.
R = 0.082 L*atm/mol*K.
Step-by-step solution:
This is an ideal gas law problem. The ideal gas law is a single equation which relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of an ideal gas. The formula of the ideal gas is given by the following:
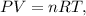
where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the constant of ideal gas, and T is temperature.
We want to find the number of moles of air present in the cylinder, so we have to solve for 'n' and replace the given data, like this:
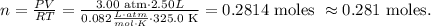
The answer is that we have 0.281 moles of the present air.