The equilibrium constant Kc is the value that relates the molar concentrations of reactants and products. For a reaction with the following general balanced equation: aA+bB-->cC+dD, the value of the constant in equilibrium will be:
![Kc=\frac{{}[C\rbrack^c[D\rbrack^d}{[A]^a[B]^b}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/f6o76n4mj9ol46quenyuhr4bmxe9w6yhfs.png)
The square brackets represent the molar concentrations of the compounds.
Now, for this reaction we have 1 reactant and 1 product (aA--->cC), the equilibrium equation will then be:
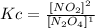
If we replace the molar concentrations we will then have Kc:
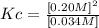
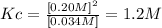
Answer: The numerical value of Kc of the reaction is 1.2M