The range of a function is the set of all values that it can take when its independent variable takes values on the domain.
On the other hand, the range of a function is the domain of its inverse function, if that inverse exists, and vice-versa: the domain of a function is the range of its inverse function, if that inverse exists.
In the case of the given equation:
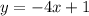
The inverse function exists since the function is linear, and it can be found by isolating x:
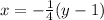
If the range of the original function is the set given by the number {