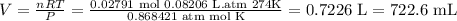Answer
A) 722.6 mL
Procedure
To solve this problem we can use the ideal gas Law given the temperature and pressure conditions.
Data
R= 0.08206L⋅atm⋅K⁻¹⋅mol⁻¹
P= 1.20 atm
T=112 °C =385.15 °K
V=0.735 L
Formula
PV=nRT
Solving for n to get the moles we will have
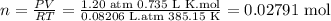
Once we have calculated the moles we solve again with the new temperature and pressure conditions, remember to use the units of R constant. Pressure in atm and temperature in Kelvin for this case.
Data
n=0.02791 mol
R= 0.08206L⋅atm⋅K⁻¹⋅mol⁻¹
P= 660 mmHg = 0.868421 atm
T=274 °K
Solve for V