Answer: the pH of the given solution is 9.4 and the pOH is 4.6
Step-by-step explanation:
The question requires us to calculate the pH and pOH values of an aqueous solution that presents a concentration of H+ ions of 3.6 x 10^-10 M.
By definition, the pH of a solution can be calculated applying the negative logarithm of the H+ ions in solution, as it follows:
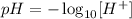
(where [H+] corresponds to the concentration of H+ ions in solution)
Thus, we can determine the pH of the solution provided by the question as:
![\begin{gathered} pH=-\operatorname{\log}_(10)[H^+\rbrack \\ \\ pH=-\log_(10)(3.6*10^(-10))=9.4 \end{gathered}]()
Therefore, the pH of the solution is 9.4.
Similarly, the pOH of a solution can be calculated as the negative logarithm of the OH- ions concentration in solution. Since the question does not provide the concentration of OH- ions, we can apply a different equation, which comes from the self-ionization of water.
The equilibrium constant for the self-ionization of water (a reaction where water dissociates into H+ and OH- ions) is 1.0 x 10^-14. Based on this, we can write that:
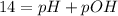
And, with the calculated value of pH (pH = 9.4), we can determine the pOH value of this solution:
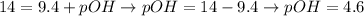
Therefore, the pOH of the solution is 4.6.
In summary, the pH of the given solution is 9.4 and the pOH is 4.6.