The given expression is
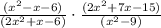
We have to factor all the expressions, one by one.
First expression.
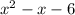
Let's use the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/rxvf73usjbbwyik14knxdemoz21vfz2ufc.png)
Where a = 1, b = -1, and c = -6.
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-(-1)\pm\sqrt[]{(-1)^2-4(1)(-6)}}{2(1)}=\frac{1\pm\sqrt[]{1+24}}{2}=\frac{1\pm\sqrt[]{25}_{}}{2}=(1\pm5)/(2) \\ x_1=\frac{1+5_{}}{2}=(6)/(2)=3\to(x-3) \\ x_2=(1-5)/(2)=(-4)/(2)=-2\to(x+2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/qvoz8g2pi3i1h3dvggcfsd6unex6tny6u7.png)
So, the expression in factored form is (x+2)(x-3).
Second expression.
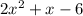
Where a = 2, b = 1, and c = -6. Let's repeat the process.
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{1^2-4(2)(-6)}}{2(2)}=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{1+48}}{4}=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{49}}{4}=(-1\pm7)/(4) \\ x_1=(-1+7)/(4)=(6)/(4)=(3)/(2)\to(2x-3) \\ x_2=\frac{-1-7_{}}{4}=-(8)/(4)=-2\to(x+2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/30x29ar5dbcn10ltfb0l69r22x14mdabox.png)
So, the expression in factored form is (2x-3)(x+2).
Third expression.
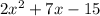
Where a = 2, b = 7, and c = -15.
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-7\pm\sqrt[]{7^2-4(2)(-15)}}{2(2)}=\frac{-7\pm\sqrt[]{49+120}}{4}=\frac{-7\pm\sqrt[]{169}}{4}=(-7\pm13)/(4) \\ x_1=(-7+13)/(4)=(6)/(4)=(3)/(2)\to(2x-3) \\ x_2=(-7-13)/(4)=(-20)/(4)=-5\to(x+5) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mvn6djm47dbr09ianu66r2d0o4b9p3fpti.png)
The expression in factored form is (2x-3)(x+5).
Fourth expression.
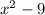
In this case, we have a difference between perfect squares, which can be solved using the following.
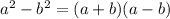
Where a^2 = x^2 and b^2 = 9.
![b^2=9\to b=\sqrt[]{9}\to b=3](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/xqqnrrkvep2p0rv3dsqtjwcp4gxk6ub5vu.png)
So, the expression in factored form is (x+3)(x-3).
Once we have all the factored forms, we simplify.
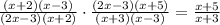
Therefore, the numerator is x+5, and the denominator is x+3.