Given the two functions below
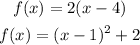
In other to determine whether the functions are inverse, we would find the inverse of both functions as shown below
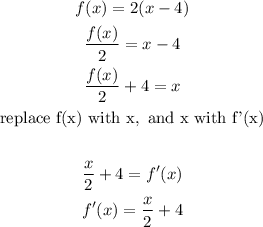
![\begin{gathered} f(x)=(x-1)^2+2 \\ f(x)-2=(x-1)^2 \\ \sqrt[]{f(x)-2}=x-1 \\ \sqrt[]{f(x)-2}+1=x \\ \text{replace f(x) with x},\text{ and x with f'(x)} \\ \sqrt[]{x-2}+1=f^(\prime)(x) \\ f^(\prime)(x)=\sqrt[]{x-2}+1 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wzp4ceg51ep7ad6eimizqt8b2kdru40441.png)
It can be observed from the inverse function that none of the inverse functions is equal to the original function of the given question
Hence, the functions are not inverses