a) We have to find the equation of the quadratic expression.
We have the expression:
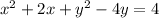
We can grouop the terms for y and x and find the constants we need to form a perfect binomial (completing the squares):
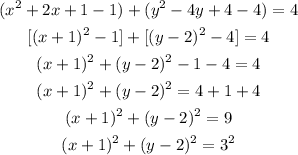
The expression results in a circumference of radius 3 with the center ar (-1,2).
c) If we have the equation:
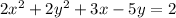
We can solve this as:
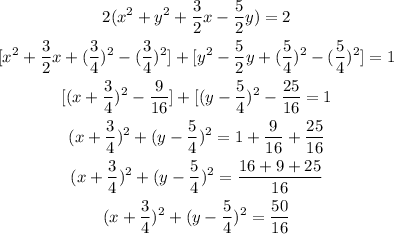
We can calculate the radius as:
![r=\sqrt[]{(50)/(16)}=\sqrt[]{(2\cdot25)/(16)}=\sqrt[]{2}\cdot(5)/(4)=(5)/(4)\sqrt[]{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/44v6q76y2bv4c6rwyqzuc59pyb6imx8ccf.png)