To answer, we will first need to use the Law of cosines. Assuming the angles ∠A, ∠B and ∠C are opposite to the sides a, b, and c, we can use the formula of the Law of Cosines to find the missing side:
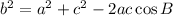
Thus, we have:
m∠B = 111°
a = 12
c = 6
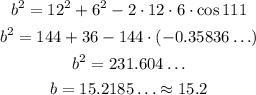
Now that we know all sides and one of the angles, we can use the Law of Since:
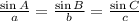
Thus:
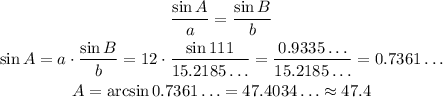
And:
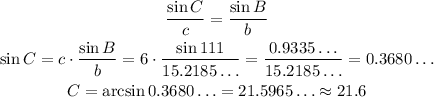
So, we have:
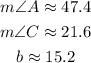
Which corresponds to the first alternative.