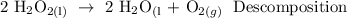
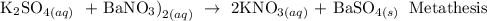
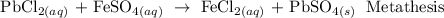
A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which one reactant breaks down into two or more products.
A metathesis reaction is a chemical reaction in which the positive ions and negative ions present in the reactants appear to exchange partners.