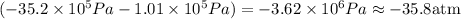ANSWERS
1. 13 m³
2. v2 = 86.25 m/s
3. -35.8 atm
Step-by-step explanation
1. The volume of water flowing in a 8min period is
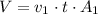
Where v1 = 13.8m/s, t = 8min and A1 is the section of the pipe:
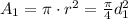
So the volume is (remember to transform the time from minutes to seconds and the diameter from centimeters to meters)
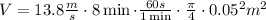
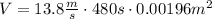
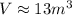
2. The speed in the left section of the pipe is
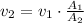
This is because the flow rate is constant along the pipe (Q = v*A).
As shown in the previous item the area is
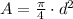
So when dividing both areas the factor π/4 cancels out. Therefore the speed is
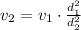
In this case we can use centimeters for the diameters because in the division the units cancel out
![v_2=13.8m/s\cdot\frac{5^2\operatorname{cm}}{2^2\operatorname{cm}}=13.8m/s\cdot(25)/(4)=86.25m/s]()
3. Using Bernoulli's equation:
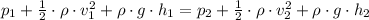
The pipe is horizontal so h1 = h2. Also, the pipe is open on the right side p1 = p0, where p0 is atmosferic pressure. The third term on each side of the equation cancels out because they are equal:
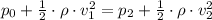
Solving for p2:
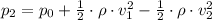
1/2 and ρ are common factors:
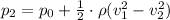
Atmosferic pressure is given 1.01x10⁵ Pa, ρ is also given 1000 kg/m³. The speeds are v1 = 13.8m/s and v2 = 86.25 m/s. The pressure in the left section of the pipe is
![p_2=1.01*10^5Pa+(1)/(2)\cdot1000\frac{\operatorname{kg}}{m^3}\cdot(13.8^2-86.25^2)(m^2)/(s^2)]()
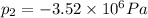
Thus, the guage pressure in the left section of the pope is: