Step-by-step explanation:
Data provided:
T2 = 40.0 °C
(absolute temperature = T2 = 40.0 °C + 273 = 313 K)
------
T1 (absolute) = 20.0 °C + 273 = 293 K
------
The rate constant for a reaction at 40.0 °C is exactly 4 times that at 20.0 °C, mathematically:
k2/k1 = 4
------------------------
Here is used the Arrhenius expression as follows:
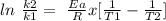
R = universal gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
Ea = activation energy
------------------------
Procedure:
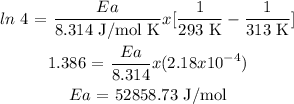
Answer: Ea = 52858.73 J/mol