We have the next given function:
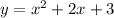
The equation corresponds to a parabola.
First, we need to derivate it:
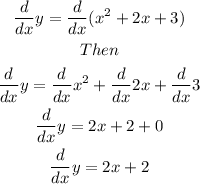
Now, we need to find when x=0.
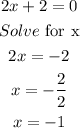
So, we can check the numbers using the number line:
Now, we need to check a number smaller than -1 and another number greater than -1.
Let us check 3.
Then:
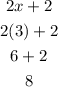
POSITIVE, when the x value is greater than -1, the function is positive (it is increasing).
Let us check -2:
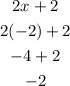
NEGATIVE, when the x value is smaller than -1, the function is decreasing.
Finally, we can write each interval.
The function is decreasing on interval (-∞,-1)
The function is increasing on interval (-1,∞)