Given data:
* The actual length of the iron rod is 30 cm.
* The initial temperature is 20 degree celsius.
* The final temperature is 80 degree celsius.
* The mass of the iron rod is 3 kg.
* The value of constants are,
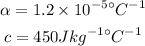
Solution:
(a). The increase in the length of the iron rod with the change in the temperature is,
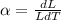
where L is the actual length, and dL is the change in the length,
Substituting the known values,
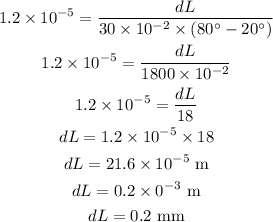
Thus, the change in the length of the iron rod is 0.2 mm.
Hence, first option is the correct answer.