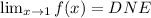The function f is given by:
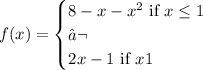
Therefore,
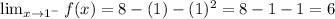
Therefore,
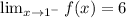
Hence, the limit of f(x) as x tends to 1 from the left is 6
![\begin{gathered} \lim_(x\to1^+)f(x)=2(1)-1=1 \\ \operatorname{\lim}_(x\to1^+)f(x)=1 \end{gathered}]()
Hence, the limit of f(x) as x tends to 1 from the right is 1
Since the left limit is not equal to the right limit, it follows that the limit of f(x) as x tends to 1 does not exist: