The given functions are
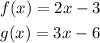
Let's find the quotient between these functions
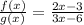
The domain of this new function is determined by the denominator 3x-6 because it can't be equal to zero.
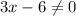
Let's solve for x
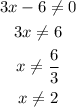
This means the domain must have a restriction.
Therefore, the domain would be
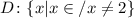
In words, the domain of the function is all real numbers except the number 2.