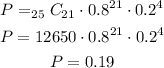This situation can be modeled by the binomial distribution, because there are two outcomes: a nurse can respond or a nurse cannot respond. The probability, p, that a nurse can respond is 0.8 (or 80%), the probability, q, that a nurse cannot respond is 0.2 (= 1 - 0.8). In 25 trials, we need that in 21 of them a nurse can respond.
The binomial distribution formula is:
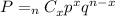
where xCn means number of combinations, n is the number of trials, x is number of times for a specific outcome within n trials, p is the probability of succes, and q is the probability of failure.
Substituting with n = 25, x = 21, p = 0.8 and q = 0.2, we get: