Answer:
To find an inverse function, reflect a graph of a function across the line y=x (and find the resulting equation)
To reflect a linear function in the line y=x, find points on f(x) and then swap their x and y coordinates.
Points on f(x): (0, -4) (2, 0) (5, 6)
Points reflected in line y=x: (-4, 0) (0, 2) (6, 5)
Plot points (-4, 0) (0, 2) (6, 5) and connect to form a straight line - this is the inverse of the function:
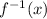
To determine the equation of f(x):
Choose 2 points on f(x): (5, 6) and (0, -4)
Calculate the slope (gradient) by using:
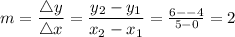
Using the slope-intercept form: y = mx + b
(where m is the slope and b is in the y-intercept)
From inspection of the graph, we can see the line crosses the y-axis at -4,
⇒ f(x) = 2x - 4
As the line is actually a line segment (with endpoints (0, -4) and (5, 6), then
f(x) = 2x - 4, 0 ≤ x ≤ 5
To determine the equation of
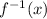 :
:
Rewrite f(x) as
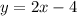
Swap the x and y:
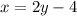
Rearrange to make y the subject:
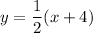
Replace y with
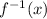
So the equation of the inverse is:
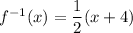
As the original function is a segment, then
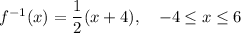
(shown in blue on the attached diagram)
** I can't see any points labelled E and F on the original function. If they are the endpoints of the line segment of f(x), then they are (0, -4) and (5, 6) **