Answer
The radius of the circle is 15
Step-by-step explanation
Problem Statement
The question gives us a circle with two chords LM and JK that are equal in length and line segments NQ = 7x - 12 and NP = 3x. We are asked to find the radius of the circle.
Solution
- We have chord LM intersecting with line NQ at a right angle and chord JK intersecting with line NP at a right angle as well. This means we can apply the Chord and line segment theorem.
- This theorem states that "If a chord intersects a line drawn from the center of the circle, at a right angle, then the line bisects the chord into two equal parts."
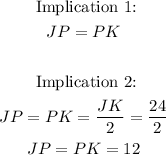
- The implication of this theorem is that:

- The same theorem can be applied to line NP and chord JK. And we shall reach similar conclusions. That is:
- We can redraw the circle to get a better understanding as shown below:
- Observe that NLQ and NJP form right-angle triangles. The hypotenuse of both triangles is indicated as r, which is also the radius of the circle. This means that we can apply the Pythagoras' theorem.
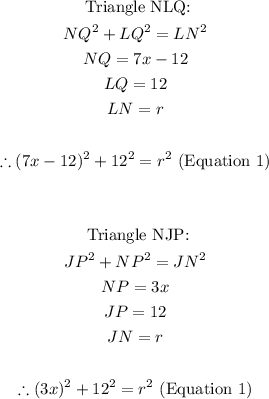
- Notice that the two equations above, equate to r-squared. This means that they are equal to each other. When we equate them, we can get the value of x.
![\begin{gathered} (7x-12)^2+12^2=r^2 \\ (3x)^2+12^2=r^2 \\ \\ \therefore(7x-12)^2+12^2=(3x)^2+12^2 \\ \text{Subtract }12^2\text{ from both sides} \\ (7x-12)^2=(3x)^2 \\ \text{Take the squre root of both sides} \\ \sqrt[]{(7x-12)^2}=\sqrt[]{(3x)^2^{}} \\ \\ 7x-12=3x \\ \text{subtract 3x from both sides and add 12 to both sides} \\ 7x-3x=12 \\ 4x=12 \\ \text{Divide both sides by 4} \\ (4x)/(4)=(12)/(4) \\ \\ \therefore x=3 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/4yteaiq0fcdt0ds8aea2795zv4o3q4x0bb.png)
- Now that we have the value of x, we can find the value of the radius (r) using any of the two equations from above.
- The value of radius (r) is gotten as follows:
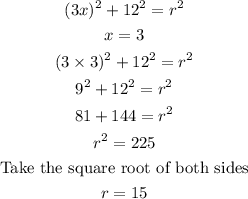
Final Answer
The radius of the circle is 15
-