We are given the following expression:
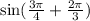
the identity for the sum of angles for sines is the following:
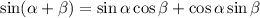
In this case, we have:
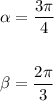
Substituting in the identity we get:
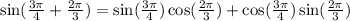
we have the following value:
![\sin ((3\pi)/(4))=\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yko21km6leskdi8zq5jpvtu1c0n91w6yos.png)
![\cos ((3\pi)/(4))=-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/47p3vgonikp52rv2eudu8wohy596tzhsf3.png)
![\sin ((2\pi)/(3))=\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yady7pt4zm1n8khohdv3aiz603l1oqtqyz.png)
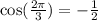
Now, we substitute the values in the indentity:
![\sin ((3\pi)/(4))\cos ((2\pi)/(3))+\cos ((3\pi)/(4))\sin ((2\pi)/(3))=(\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}})(-(1)/(2))+(-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}})(\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2})](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/d6xdltf2o3know0raqg10smj7yhai2afbj.png)
Simplifying we get:
![(\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}})(-(1)/(2))+(-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2}})(\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2})=-\frac{1}{2\sqrt[]{2}}-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2\sqrt[]{2}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ou50cweoki7mf4aynck2vzzc205c8d8v27.png)
Solving the operations:
![-\frac{1}{2\sqrt[]{2}}-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2\sqrt[]{2}}=-0.97](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/15hmi8sj4bo9vy4wdvcb4v84iz7pbrmlh0.png)
Therefore, the value of the sine is -0.97