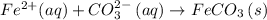Answer
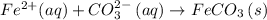
Step-by-step explanation
The given equation is:
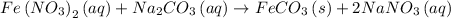
What to find:
To write the net ionic equation, including phases, that corresponds to the given reaction.
Step-by-step solution:
Going through the given equation, the equation is balanced molecularly. and the phases indicated.
The next step is split the electrolytes into ions (that is, to write the complete ionic equation).
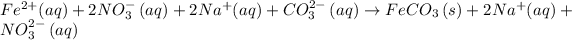
Cross the spectator ions on both sides of the complete ionic equation. (Spectator ions are ions that are unchanged on both sides of the complete equation).
Hence, the net ionic equation, including phases, that corresponds to the reaction given will be: