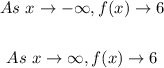Solution
Asymptote:
Vertical Asymptote
- The vertical asymptotes of a rational function are determined by the denominator expression.
- The expression given is:
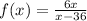
- The denominator of (x- 36) determines the asymptote line.
- The vertical asymptote defines where the rational function isundefined. Iin order for a rational function to be undefined, its denominator must be zero.
- Thus, we can say:
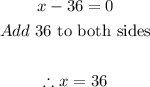
- Thus, the vertical asymptote is
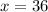
Horizontal Asymptote:
- The horizontal asymptote exists in two cases:
1. When the highest degree of the numerator is less han the degree of the demnominator. In this case, the horizontal asymptote is y = 0
2. When the highest degee sof the numerator and tdenominator are the same. In this case, the horizontal asymptote is
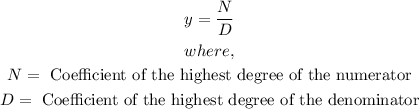
- For our question, we can see that the highest degrees of the numerator and denominator are the same. Thus, we have the Horizontal Asymptote to be:
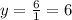
End behavior:
- The end behavior is examining the y-values of the function as x tendsto negative and positive infinity.
- Thus, we have that:
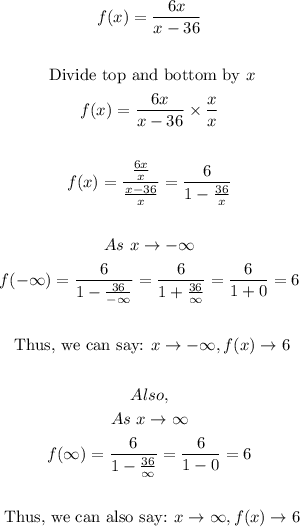
Final Answers
Asymptotes:
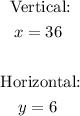
End behavior: