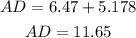We have 2 right triangles, so we can apply a trigonometric function in order to obtain AC and CD.
If we apply cosine funcion in triangle ABC, we get
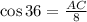
therefore, AC is equal to
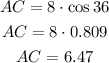
Now, we can apply Pitagorean theorem on triangle ABC in order to find BC, that is
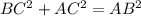
then, we have
![BC\questeq\sqrt[]{AB^2-AC^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/4tsshv04635dtkz62de88dur5hamju5glh.png)
If we substitute AB=8 and AC=6.47, we obtain
![\begin{gathered} BC=\sqrt[]{8^2-(6.47)^2} \\ BC=\sqrt[]{64-41.96} \\ BC=\sqrt[]{22.14} \\ BC=4.71 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/udma60ypyauplra1qammst8vnwd2rmpnpo.png)
Now, we can draw the following triangle:
So, in order to find CD we can apply Pitagorean theorem again, that is
![\begin{gathered} CD^2+BC^2=BD^2 \\ CD=\sqrt[]{BD^2-BC^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/sj9hwyytgc93hwdikfodwn3ucrlznvr9cn.png)
By substituting the values, we get
![\begin{gathered} CD=\sqrt[]{7^2-(4.71)^2} \\ CD=\sqrt[]{49-}22.1841 \\ CD=\sqrt[]{26.82} \\ CD=5.178 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/i8zbkjgy5irf6grm0r1z5te2dn5wq7to39.png)
Therefore, the length AD=AC+CD, then the answer is