Answer:
y'=6x-2
Explanation:
Given the function:
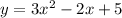
We want to find the derivative using the increment method.
First, replace y with y+△y and x with x+△x.
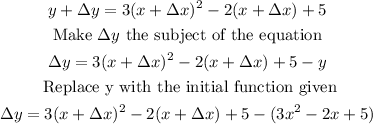
Next, simplify the right-side of the equation:
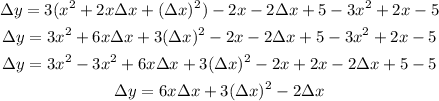
Factor out △x in the right-side of the equation:
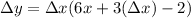
Divide both sides by △x:
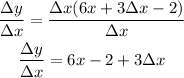
Let △x tends to 0:
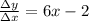
The derivative of y is 6x-2.