Given the functions:
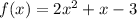
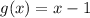
You need to multiply them in order to find:
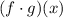
Then, you need to set up:
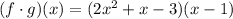
Now you need to simplify it by applying the Distributive Property:
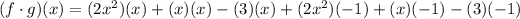
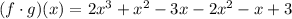
Adding the like terms (the terms that have the same variable with the same exponent), you get:
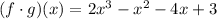
By definition, the Domain of a function is the set of all the possible input values for which the function is defined.
In this case, you can identify that the function obtained is a Polynomial Function because all its exponents are positive integers. By definition, the domain of all Polynomial Functions is:
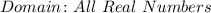
Hence, the answer is: First option.