Answer
Step-by-step explanation
Given that:
The normal freezing point of the solvent X, T₁(solvent) = -6.70 °C
The freezing point of the solution, T₂ = -10.9 °C
The freezing point depression constant, Kf = 2.22 °C.kg/-mo
Mass of solvent X = 500.0 g = 0.50 kg
What to find:
To calculate the mass of C₂H5NO₂ that was dissolved.
Step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Calculate the freezing point depression, ΔTf.
The freezing point depression, (ΔTf) can be calculated using:
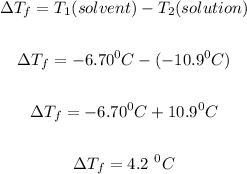
Step 2: Calculate the molal concentration of the solution.
The molality of the solution can be determined using:
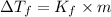
Where m is the molality of the solution.
Putting ΔTf = 4.2 °C, Kf = 2.22 °C.kg/mol, the molality of the solution is:
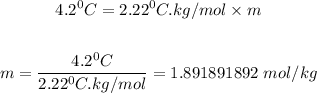
Step 3: Determine the mass of C₂H5NO₂ that was dissolved.
The mass of C₂H5NO₂ that was dissolved can be calculated using the formula for molality below:
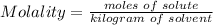
Molality = m = 1.891891892 mol/kg, kilogram of solvent = mass of X = 0.5 kg.
So,
