The initial equation is:
2(3x + 5) - 2x + 2 = 0
By distributive property:
2(3x) + 2(5) - 2x + 2 = 0
6x + 10 - 2x + 2 = 0
Then, we sum the terms with an x and the terms without an x, as:
(6x - 2x) + (10 + 2) = 0
4x + 12 = 0
Subtracting 2 on both sides:
4x + 12 - 12 = - 12
4x = - 12
Dividing by 4 on both sides of the equation:
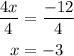
Answer: x = -3