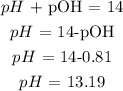Answer:
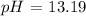
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to calculate the pH of the given solution
Since the alkali is a strong one, dissociation is complete
That means the molarity of the solution equals the molarity of the hydroxide ions
Now, let us calculate the pOH
Mathematically:
![\begin{gathered} pOH\text{ = -log\lbrack OH}^-] \\ pOH\text{ = -log\lparen0.155\rparen} \\ pOH\text{ = 0.81} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/h3nsa5br5eldwmdtm9w5j90wwoef7k0mst.png)
Furthermore: