The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is an equation in the form:
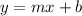
Where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Comparing the given equation with the model, we can see that the equation y = -3/4x + 3 is already in the slope-intercept form, where m = -3/4 and b = 3.
The y-intercept is a point in the form (0, b), so the y-intercept in this case is (0, 3).
In order to calculate the x-intercept, we just need to use y = 0, so we have:
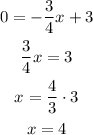
So the x-intercept is the point (4, 0).