Here are the steps in determining the critical values in a chi-square distribution.
a. Since the number of rows and columns are not provided in the question, we subtract 1 from the sample size to determine the degrees of freedom.
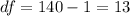
The degree of freedom is 13.
b. Since this is a two-tailed test, subtract 0.98 from 1 and then divide the result by 2.
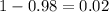
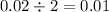
Let's look at the probability of 0.01 on both the upper and lower tails of the distribution with df = 13.
Please refer to the chi-square distribution table.
Based on the table, the lower critical value at df = 13 with a probability of 0.01 is 4.107 while the upper critical value is 27.688.