Answer: If the volume of a gas is increased at a constant temperature, the pressure of the gas decreases.
Explanation:
The relation between variation in volume and variation in pressure of a gas at a constant temperature is given by Boyle's Law which states that: The product of pressure and volume of a mass of a contained gas is constant at a constant temperature.
That is,
Pressure (P) x Volume (V) = constant (k)
[when the temperature (T) is constant; k ≠ 0.]
Or, P =
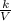
That is, pressure varies inversely with volume or an increase in volume at a constant temperature causes a decrease in the pressure of the gas.
Detailed answer:
- Gas molecules are always in random motion, and the pressure of a gas is defined as the pressure exerted by these moving gas molecules on the walls of the container as they undergo collisions with the walls of the container.
- The volume of a gas is defined as the three-dimensional space occupied by all the gas molecules in the container at a particular temperature and pressure.
- Thus, when the volume increases keeping the temperature constant (thus no change in kinetic energy of the molecules occurs due to temperature), the molecules get more space to move around. Thus the pressure exerted by the molecules on the walls of the container decreases.