Given the equation:
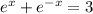
We have the following equivalent expression:
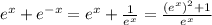
then, substituting in the first equation, we have:
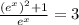
since e^x is always positive, we can multiply both sides by it to get:
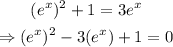
then, if we make u = e^x, we get the following quadratic equation:
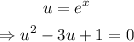
which have the following solutions:
![\begin{gathered} u_1=\frac{3_{}+\sqrt[]{5}}{2} \\ u_2=\frac{3-\sqrt[]{5}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8d2ddipdoxaccvf0thqnzi24iu35vux0i1.png)
then, by reversing the substiution of u = e^x, we get:
![\begin{gathered} e^x=\frac{3\pm\sqrt[]{5}}{2} \\ \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/foa5sfx9bf8shq29wh35irvryez0t71iat.png)
finally, using the natural logarithm on both sides of the equation, we get the following:
![\begin{gathered} \ln (e^x)=\ln (\frac{3\pm\sqrt[]{5}}{2}) \\ \Rightarrow x=\ln (\frac{3\pm\sqrt[]{5}}{2}) \\ \Rightarrow x_1=\ln (\frac{3+\sqrt[]{5}}{2})=0.96 \\ \Rightarrow x_2=\ln (\frac{3-\sqrt[]{5}}{2})=-0.96 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/lgeeidwgaqeyqwiaftonb7neib2l8ymkhc.png)
therefore, the solution of the exponential equation is x = ln(3 + sqrt(5)/2) = 0.96 and x = ln(3-sqrt(5)/2) = -0.96