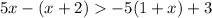
We can begin by eliminating the parentheses by distributing the terms:
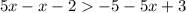
Reducing like terms at either side of the equation:
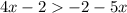
Adding 2 at both sides:
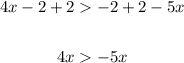
Now adding 5x at both sides:
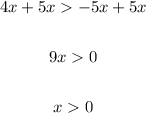
Then, the solution for the inequality is the set of all real numbers higher than 0 (excluding it).
We can represent this in the number line by highlighting all positive numbers and drawing a void circle at 0 to indicate that the solution does not include it: