$ 35750
Step-by-step explanationThe formula to calculate total cost is the following:
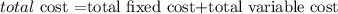
so
Step 1
in this case, the variable cost is the cost from the watches ( because it depends on the number of watches produced)
hence
a)let
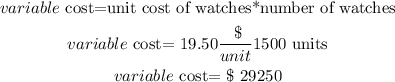
and
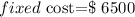
b) finally, replace in the formula
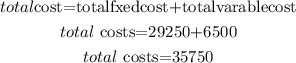
therefore, the answer is
$ 35750
I hope this helps you