The mass of H2 is 2.62x10^-3 g.
To calculate the mass of H2 we can use the Ideal Gas formula:
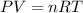
P is the pressure of the gas (atm).
V is the volumen of the gas (L).
n is the number of moles of the gas.
R is the gas constant (0.082 atm.L/mol.K)
T is the temperature of the gas (K).
- First, we need to assume that the pressure is 1 atm, as this information is not given. Then, we have to do the units change so that everything is in the units of the R constant (atm.L/mol.K).
In this case:
P = 1 atm
V= 0.0331 L
T = 308 K
- Second, the number of moles can be calculated from the Ideal Gas formula:m
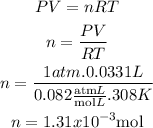
So far, we know that there are 1.31x10^-3 moles of H2.
- Finally, we can calculate the H2 mass from its the molar mass and a mathematical Rule of Three:
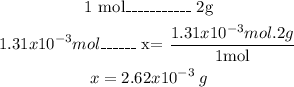
So, the mass of H2 is 2.62x10^-3 g.