Solution
For this case we can do the following:
![f(x)=2\sqrt[]{x+1}-3](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9r3mt32mspjy4bisypn78kghfxifeq4wr2.png)
We can find:
f(0)= -1 , f(3) = 1
And we have:
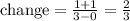
For the new function g(x) we have:
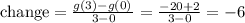
And for h(x) we have:
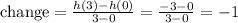
For this case we can conclude that the greater rate of change needs to be g(x) no matter if is negative since we need to analyze the absolute value