From the identity
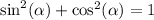
we can find the value for sin(α). Using our value for the cosine and solving the identity for sin(α), we have
![\begin{gathered} \sin ^2(\alpha)+((7)/(9))^2=1 \\ \sin ^2(\alpha)=1-((7)/(9))^2 \\ \sin ^2(\alpha)=1-(7^2)/(9^2) \\ \sin ^2(\alpha)=1-(49)/(81) \\ \sin ^2(\alpha)=(81)/(81)-(49)/(81) \\ \sin ^2(\alpha)=(32)/(81) \\ \sin (\alpha)=\pm_{}\sqrt[]{(32)/(81)} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/bst1chuk1a0rmfb6vnkhxiwp85843qrnzi.png)
Since sin(α) < 0, we have
![\sin (\alpha)=-_{}\sqrt[]{(32)/(81)}=-\frac{4\sqrt[]{2}}{9}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/hdvu22hs1re9hikcb7s6ith2efib2b8aln.png)
The cot(α) is defined as the ratio between the cosine and sine of alpha.
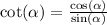
Then, the cot(α) is
![\cot (\alpha)=\frac{(7)/(9)}{-\frac{4\sqrt[]{2}}{9}}=-\frac{7}{4\sqrt[]{2}}=-\frac{7\sqrt[]{2}}{8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/xelsi20zshow4mp0zjjztacxue2tgz35ft.png)
This is the exact value of cot(α).
![\cot (\alpha)=-\frac{7\sqrt[]{2}}{8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/jrbas1663pj9tobht6ld3jw9bpnylo8n4n.png)