In this case we can use the exponential growth model, given by
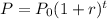
where P_0 is the inital population, r is the rate and t the time. In our case, we have
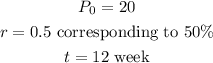
So, by substituting these values into the model, we have
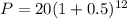
which gives
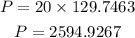
Therefore, by rounding off to the nearest whole number, the answer is 2595 bacteria