Chemistry => The Behavior of Gases => Ideal Gas
The work produced by gas can be defined as the product of the volume and the pressure (PV). We are told that the pressure and temperature throughout the expansion are equal to 1.05bar and 22.4°C respectively. So we must find the volume of gas produced.
By means of the reaction equation, we can see that the reactants are not gaseous, so we can assume that the volume of the gas before the reaction is zero and that the final volume will correspond to the volume of H2 produced.
To find the volume we will assume that the gas behaves as an ideal gas, we will first find the moles of H2 produced and apply the ideal gas law.
To find the moles of H2 produced we will do:
1. Convert the 10.5 grams of magnesium to moles by dividing by the molar mass of magnesium, 24.305g/mol.
2. As Mg is the limiting reactant, we find the moles of H2 with the stoichiometry of the reaction. The ratio H2 to Mg is 1/1.
So, the moles of H2 will be:
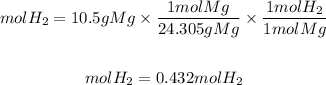
Now, to find the work done by the gas we will use the ideal gas law that says:
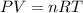
The term PV will be the work done by the expansion
n is the moles of H2 produced
R is the constant 8.314x10^-2LBar/Kmol
T is the temperature in Kelvin, 22.4°C = 295.55K
So, the work done will be:
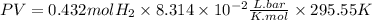
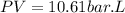
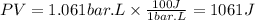
As the gas is doing an expansion the work will be positive.
Answer: d. +1061 J