To find the points at which the tangent line is horizontal, it is enough to find where the slope of the function is 0 because a horizontal line's slope is 0.
Find f'(x).
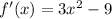
Now set it equal to 0 and solve for x to find the x values at which the tangent line is horizontal to given function.
![\begin{gathered} 3x^2-9=0 \\ 3x^2=9 \\ x^2=3 \\ x=\pm\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/f8v69dlr0i54rsi4n2lt2qvrvs1tlbears.png)
Find the function values at these x-values.
![\begin{gathered} f(\sqrt[]{3})=(\sqrt[]{3})^3-9\sqrt[]{3} \\ =3\sqrt[]{3}-9\sqrt[]{3} \\ =3\sqrt[]{3}(1-3) \\ =-6\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/tcrcd05zbhg121e5kliivdzgn8e56w54vw.png)
![\begin{gathered} f(-\sqrt[]{3})=(-\sqrt[]{3})^3+9\sqrt[]{3} \\ =-3\sqrt[]{3}+9\sqrt[]{3} \\ =3\sqrt[]{3}(-1+3) \\ =6\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/tgdaf02xjbqcsduq1eyv2z54hwsc1djenr.png)
The points where the graph of the function have horizontal tangents are
![(\sqrt[]{3},-6\sqrt[]{3}),(-\sqrt[]{3},6\sqrt[]{3})](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/vfc7xcvzg6mlyszec0ait7onsw2kvzdojj.png)
Option A is correct.