Explanations:
- The subatomic particle is the total number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the nucleus of the carbon-14 atom.
A carbon-14 element has an atomic number of 6 and a mass number of 14. Since the atomic number of carbon is equal to the number of protons, hence the number of proton in the nucleus of the element is 6 protons.
Also, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Hence there are 6electrons in the nucleus of the carbon-14 atom.
For the number of neutrons, we can use the relationship;
Mass number = number of proton + neutron
14 = 6 + number of neutron
number of neutron = 14 - 6 = 8 neutrons.
Hence, the number of subatomic particles in carbon-14 are 6 protons, 6 electrons, and 8 neutrons.
- The isotopes of carbon are carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. Among these isotopes of carbon, carbon-12, carbon-13 are more stable while carbon-14 is unstable and weakly radioactive. The unstable nature of the carbon-14 isotope is due to the presence of two extra neutrons in its nucleus.
- If the carbon-14 were to undergo beta decay, the resulting nuclear reaction that results is given as:
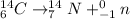
From the reaction, you can see that the daughter isotope, if carbon-14 were to undergo beta decay, is the Nitrogen-14 atom, a plain-old stable atom with seven protons and neutrons.