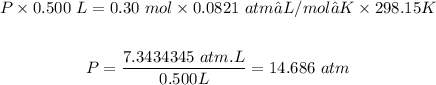Answer
The pressure inside the cylinder will change to 14.686 atm
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Volume, V = 0.500 L
Moles of O2 = 0.150 mol
Temperature, T = 25 °C = (25 + 273.15 K) = 298.15 K
Step-by-step solution:
The first step is to calculate the pressure exerted by O2 using ideal gas equation:
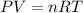
Plugging the values of the parameters into the formula:
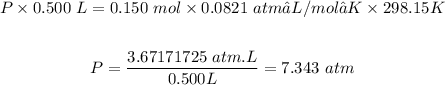
The pressure exerted by O2 = 7.343 atm
If 0.150 mol of sulfur dioxide, SO2 was added to the oxygen gas already in the cylinder, then the pressure inside the cylinder will change by a factor of 2. That is:
Total pressure will be = 2 x 7.343 atm = 14.686 atm
Or the total pressure can be calculated using the ideal equation above, and putting n = 0.150 mol + 0.150 mol = 0.3 mol