We are asked to find the mass of a gas at STP, these acronyms correspond to standard conditions and are equivalent to a pressure of 1 atm and temperature 273.15K.
Now, at these conditions we can consider that the interaction between the gas molecules is almost null so we can apply the ideal gas law which tells us:
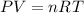
Where,
P is the pressure or the gas = 1 atm
V is the volume of the gas = 13900mL = 13.900 L
R is a constant = 0.08206 (atm L) / (mol K)
T is the temperature of the gas = 273.15 K
n is the number of moles of the gas
Now, we clear n and replace the known data into the equation:
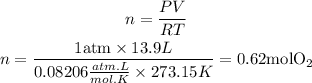
Now, with the number of moles we can find the mass of O2 using the molar mass of the molecule
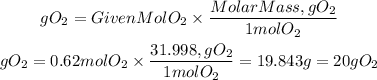
So, the mass of 13900mL of oxygen is 20g