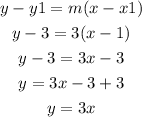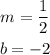
The equation of the line in the slope-intercept form is given by:
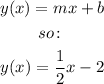
The graph of this line is given by:
----
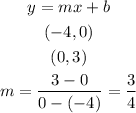
so, using the point slope equation:
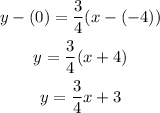
-----------------------------------
Let:
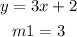
If 2 lines are parallel, then:
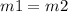
where m2 is the slope of the other line, so:
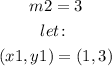
Using the point-slope equation: