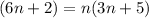
To prove if it is true for positive n intergers for induction method:
1. Prove For n=1
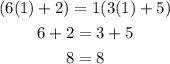
For n=1 it is true
2. Assume that the statement is true for n=k.
It is true for n=k
3. Prove For n=k+1
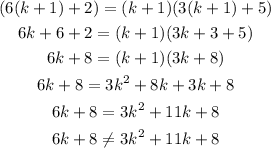
As the conjeture is not true for n=k+1
The conjeture is not true for all positive intergers