The Pythagorean Theorem can be applied in any right triangle if we are given two of the three lengths of its sides.
A right triangle forms a longer side called the hypotenuse (c) and two shorter sides called the legs (a and b).
The Pythagorean Theorem states:
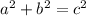
Solving for a:
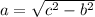
Substituting c = 25, b = 24:
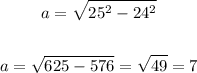
a = 7