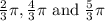Given the trigonometry equation below
![(2\cos x+1)(2\sin x+\sqrt[]{3})=0](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/m7un2p3m5399uenqovgthlxwn1hy7ds35f.png)
If two numbers multiplies themselves and the result is zero, it implies that one of them is zero or both are zero
For instance:
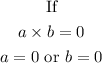
Thus,
![\begin{gathered} 2\cos x+1=0 \\ OR \\ 2\sin x+\sqrt[]{3}=0 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/v2pb95hvkhs9ktx8tmd897ydk0acmyh9bv.png)
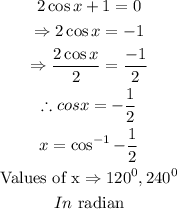
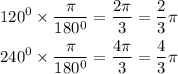
For
![\begin{gathered} 2\sin x+\sqrt[]{3}=0 \\ 2\sin x=-\sqrt[]{3} \\ \Rightarrow\sin x=-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2} \\ x=\sin ^(-1)(-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}) \\ \therefore x\Rightarrow240^0,300^0 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/bbfof6evkhghf1jg1sbeog43uepar7kejz.png)
In radian,
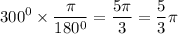
Hence, the solutions in radians of the equation in the interval [0, 2π) is